Overview of RancherOS
RancherOS is the smallest, easiest way to run Docker in production. Everything in RancherOS is a container managed by Docker. This includes system services such as udev and syslog. Because it only includes the services necessary to run Docker, RancherOS is dramatically smaller than most traditional operating systems. By removing unnecessary libraries and services, requirements for security patches and other maintenance are dramatically reduced. This is possible because, with Docker, users typically package all necessary libraries into their containers.
Another way in which RancherOS is designed specifically for running Docker is that it always runs the latest version of Docker. This allows users to take advantage of the latest Docker capabilities and bug fixes.
Like other minimalist Linux distributions, RancherOS boots incredibly quickly, generally in 5-10 seconds. Starting Docker containers is nearly instant, similar to starting any other process. This quickness is ideal for organizations adopting microservices and autoscaling.
Docker is an open-source platform designed for developers, system admins, and DevOps, it is used to build, ship, and run containers, using simple yet powerful CLI (Command Line Interface), you can get started with Docker from Docker user guide.
Hardware Requirements
- x86_64 server with at least 512MB of RAM.
Note: If you are planning on installing to disk, you will need at least 1024MB of RAM.
How this works
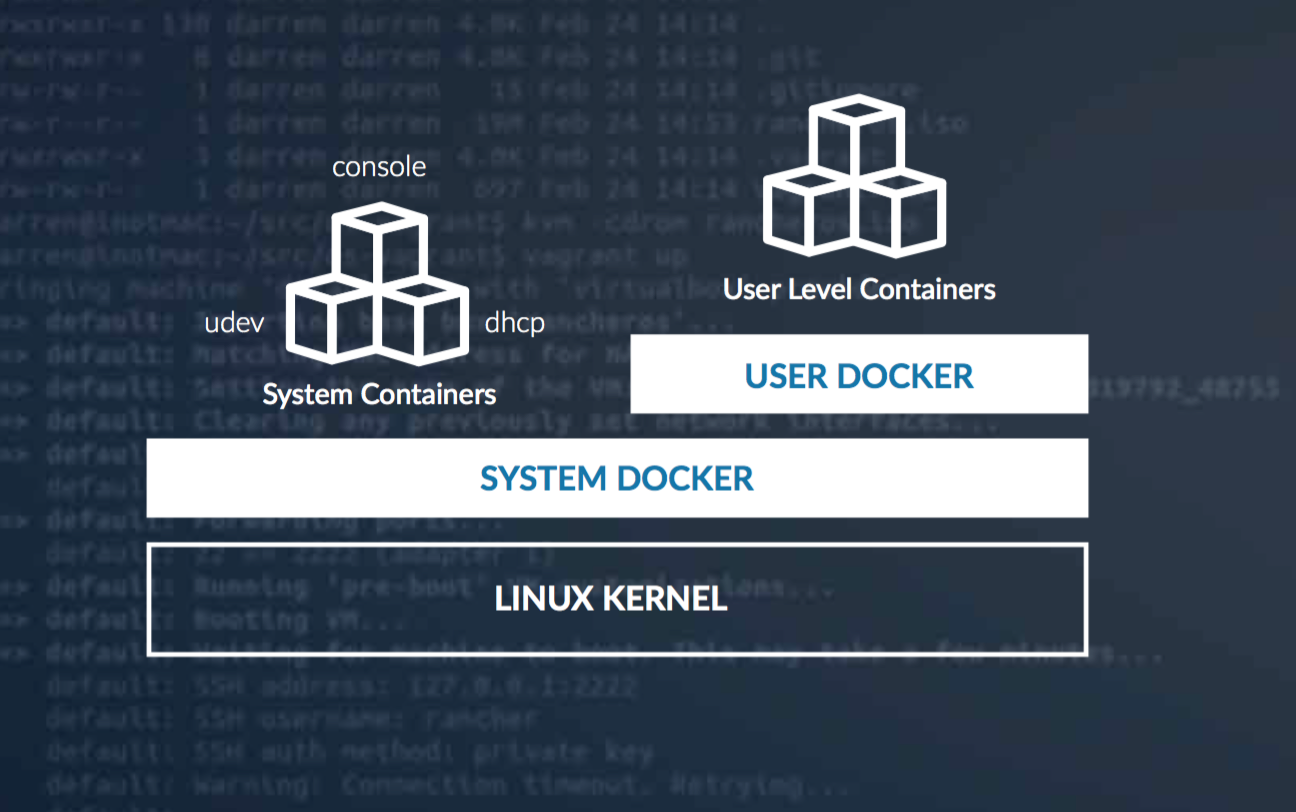
Everything in RancherOS is a Docker container. We accomplish this by launching two instances of Docker. One is what we call System Docker, the first process on the system. All other system services, like ntpd, syslog, and console, are running in Docker containers. System Docker replaces traditional init systems like systemd, and can be used to launch additional system services.
System Docker runs a special container called Docker, which is another Docker daemon responsible for managing all of the user’s containers. Any containers that you launch as a user from the console will run inside this Docker. This creates isolation from the System Docker containers, and ensures normal user commands don’t impact system services.
We created this separation because it seemed logical and also it would really be bad if somebody did
docker rm -f $(docker ps -qa) and deleted the entire OS.
Running RancherOS
To find out more about installing RancherOS, jump to our Quick Start Guide.
Latest Release
Please check our repository for the latest release in our README.